Teaching Students How to Ask Productive Questions
Improve engagement, comprehension, and critical thinking by teaching students the process of asking insightful questions.
In a recent piece for MiddleWeb, teacher and author Jackie Walsh disputes the commonly accepted classroom expectation that teachers ask the questions and students answer. “Student-generated questions put learners in the driver’s seat,” she writes. “They advance both learning and engagement.”
There are natural barriers to shifting to this more student-centered approach: “many think that asking questions might lead teachers to believe they’re not smart or suggest to their peers that they’re not cool.” But Walsh offers step-by-step guidance for addressing those issues and fostering an environment that supports questioning by students.
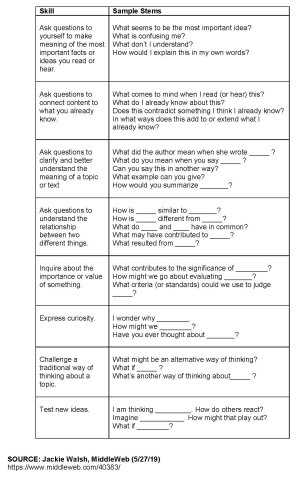
The first step is to explain why questions are critical to the learning process, Walsh says. Provide students with clear rationales such as, “I use questions to understand other perspectives and to engage in collaborative thinking and learning” or “I ask myself questions to monitor my thinking and learning.” Identifying the function of a question is crucial in motivating students, and these sample stems serve as prompts for students who need help to form useful questions.
For reference, Walsh has developed a comprehensive, metacognitive framework of questioning skills and matching prompts. The rubric makes the relationship between critical thinking and asking questions explicit and is a great handout for students.
Ultimately, though, the art of framing a question is one that must be practiced, Walsh writes. She suggests a “think time 1-2” practice, which emphasizes longer-than-normal pauses to ask and then process questions: Use a three-to-five-second pause after the teacher’s question to allow students to determine what the question is asking and whether the students understand it, and then provide a second “think time” after a student responds. The second pause “provides the opportunity for students to process what a speaker has said and pose questions about the speaker’s comment or about the topic in general.”
Other simple changes can drive home the point. Asking students, “What kinds of questions do you have?” instead of the more typical “Do you have any questions?” can send the clear signal that the torch has been passed to them. She also recommends that teachers “institute a policy of ‘raise your hand to ask a question—not to answer the teacher’s question.’” Flipping the expectation from a class where the teacher poses questions to one where students ask the questions leads to greater engagement, comprehension, and critical thinking.
