Group Work That Works
Educators weigh in on solutions to the common pitfalls of group work.
Mention group work and you’re confronted with pointed questions and criticisms. The big problems, according to our audience: One or two students do all the work; it can be hard on introverts; and grading the group isn’t fair to the individuals.
But the research suggests that a certain amount of group work is beneficial.
“The most effective creative process alternates between time in groups, collaboration, interaction, and conversation... [and] times of solitude, where something different happens cognitively in your brain,” says Dr. Keith Sawyer, a researcher on creativity and collaboration, and author of Group Genius: The Creative Power of Collaboration.
So we looked through our archives and reached out to educators on Facebook to find out what solutions they’ve come up with for these common problems.
Making Sure Everyone Participates
“How many times have we put students in groups only to watch them interact with their laptops instead of each other? Or complain about a lazy teammate?” asks Mary Burns, a former French, Latin, and English middle and high school teacher who now offers professional development in technology integration.
Unequal participation is perhaps the most common complaint about group work. Still, a review of Edutopia’s archives—and the tens of thousands of insights we receive in comments and reactions to our articles—revealed a handful of practices that educators use to promote equal participation. These involve setting out clear expectations for group work, increasing accountability among participants, and nurturing a productive group work dynamic.
Norms: At Aptos Middle School in San Francisco, the first step for group work is establishing group norms. Taji Allen-Sanchez, a sixth- and seventh-grade science teacher, lists expectations on the whiteboard, such as “everyone contributes” and “help others do things for themselves.”
For ambitious projects, Mikel Grady Jones, a high school math teacher in Houston, takes it a step further, asking her students to sign a group contract in which they agree on how they’ll divide the tasks and on expectations like “we all promise to do our work on time.” Heather Wolpert-Gawron, an English middle school teacher in Los Angeles, suggests creating a classroom contract with your students at the start of the year, so that agreed-upon norms can be referenced each time a new group activity begins.
Group size: It’s a simple fix, but the size of the groups can help establish the right dynamics. Generally, smaller groups are better because students can’t get away with hiding while the work is completed by others.
“When there is less room to hide, nonparticipation is more difficult,” says Burns. She recommends groups of four to five students, while Brande Tucker Arthur, a 10th-grade biology teacher in Lynchburg, Virginia, recommends even smaller groups of two or three students.
Meaningful roles: Roles can play an important part in keeping students accountable, but not all roles are helpful. A role like materials manager, for example, won’t actively engage a student in contributing to a group problem; the roles must be both meaningful and interdependent.
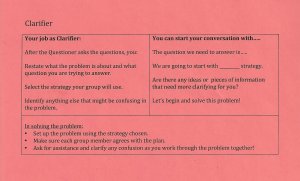
At University Park Campus School, a grade 7–12 school in Worcester, Massachusetts, students take on highly interdependent roles like summarizer, questioner, and clarifier. In an ongoing project, the questioner asks probing questions about the problem and suggests a few ideas on how to solve it, while the clarifier attempts to clear up any confusion, restates the problem, and selects a possible strategy the group will use as they move forward.
At Design 39, a K–8 school in San Diego, groups and roles are assigned randomly using Random Team Generator, but ClassDojo, Team Shake, and drawing students’ names from a container can also do the trick. In a practice called vertical learning, Design 39 students conduct group work publicly, writing out their thought processes on whiteboards to facilitate group feedback. The combination of randomizing teams and public sharing exposes students to a range of problem-solving approaches, gets them more comfortable with making mistakes, promotes teamwork, and allows kids to utilize different skill sets during each project.
Rich tasks: Making sure that a project is challenging and compelling is critical. A rich task is a problem that has multiple pathways to the solution and that one person would have difficulty solving on their own.
In an eighth-grade math class at Design 39, one recent rich task explored the concept of how monetary investments grow: Groups were tasked with solving exponential growth problems using simple and compound interest rates.
Rich tasks are not just for math class. When Dan St. Louis, the principal of University Park, was a teacher, he asked his English students to come up with a group definition of the word Orwellian. They did this through the jigsaw method, a type of grouping strategy that John Hattie’s study Visible Learning ranked as highly effective.
“Five groups of five students might each read a different news article about the modern world,” says St. Louis. “Then each student would join a new group of five where they need to explain their previous group’s article to each other and make connections to each. Using these connections, the group must then construct a definition of the word Orwellian.” For another example of the jigsaw approach, see this video from Cult of Pedagogy.
Supporting Introverts
Teachers worry about the impact of group work on introverts. Some of our educators suggest that giving introverts choice in who they’re grouped with can help them feel more comfortable.
“Even the quietest students are usually comfortable and confident when they are with peers with whom they connect,” says Shelly Kunkle, a veteran teacher at Wasawee Middle School in North Webster, Indiana. Wolpert-Gawron asks her students to list four peers they want to work with and then makes sure to pair them with one from their list.
Having defined roles within groups—like clarifier or questioner—also provides structure for students who may be less comfortable within complex social dynamics, and ensures that introverts don’t get overshadowed by their more extroverted peers.

Finally, be mindful that introverted students often simply need time to recharge. “Many introverts do not mind and even enjoy interacting in groups as long as they get some quiet time and solitude to recharge. It’s not about being shy or feeling unsafe in a large group,” says Barb Larochelle, a recently retired high school English teacher in Edmonton, Alberta, who taught for 29 years.
“I planned classes with some time to work quietly alone, some time to interact in smaller groups or as a whole class, and some time to get up and move around a little. A whole class of any one of those is going to be hard on one group, but a balance works well.”
Assessing Group Work
Grading group work is problematic. Often, you don’t have a clear understanding of what each student knows, and a single student’s lack of effort can torpedo the group grade. To some degree, strategies that assign meaningful roles or that require public presentations from groups provide a window in to each student’s knowledge and contributions.
But not all classwork needs to be graded. Suzanna Kruger, a high school science teacher in Seaside, Oregon, doesn’t grade group work—there are plenty of individual assignments that receive grades, and plenty of other opportunities for formative assessment.
John McCarthy, a former high school English and social studies teacher and current education consultant and adjunct professor at Madonna University for the graduate department for education, suggests using group presentations or group products as a non-graded review for a test. But if you want to grade group work, he recommends making all academic assessments within group work individual assessments. For example, instead of grading a group presentation, McCarthy grades each student on an essay, which the students then use to create their group presentation.

Laura Moffit, a fifth-grade teacher in Wilmington, North Carolina, uses self and peer evaluations to shed light on how each student is contributing to group work—starting with a lesson on how to do an objective evaluation. “Just have students circle :), :|, or :( on three to five statements about each partner, anonymously,” Moffit commented on Facebook. “Then give the evaluations back to each group member. Finding out what people really think of your performance is a wake-up call.”
And Ted Malefyt, a middle school science teacher in Hamilton, Michigan, carries a clipboard with the class list formatted in a spreadsheet and walks around checking in on students while they do group work.
“Using this spreadsheet, you have your own record of which student is meeting your expectations and who needs extra help,” explains Malefyt. “As formative assessment takes place, quickly document with simple checkmarks.”
