Teaching Ethics and Narrative… With Violent Video Games?
More and more teachers today are experimenting with video games in a bid to keep their classes relevant and their students engaged. It’s not uncommon to read about schools using titles like Portal 2, Minecraft, and SimCity to teach anything from high school physics to civic responsibility. These “clean,” classroom-friendly games are devoid of the graphic violence whose effects on children and adolescents have caused so much consternation and debate.
Conventional wisdom dictates that violent games have no place in schools, but this notion has been challenged by Tobias Staaby, a Norwegian high school literature and religious studies teacher who incorporates ostensibly violent games like The Walking Dead, The Last of Us, and Skyrim into his practice.
Staaby teaches at Nordahl Grieg Upper Secondary, a new state-of-the-art high school tucked away in a quiet suburb of the coastal city of Bergen. Even in a country whose progressive public education system dispenses with tests and grades until middle school and provides every high school student with a laptop, Nordahl Grieg stands out for its commitment to innovation.
Staaby attributes the school’s success to a flexible national curriculum and forward-thinking school administration. “Our principal encourages us to be daring in the use of ICT [information and communication technology] in our teaching,” he says, “and to have an entrepreneurial approach to the way we design the learning activities.” This has allowed Staaby and a group of like-minded colleagues to take bold steps in their use of video games to enrich their classes, which has quickly transformed the school into a national model for game-based learning.

Teaching Ethics in the Zombie Apocalypse
Although The Walking Dead occasionally forces players to use improvised weapons to fend off grotesque zombies, the game is primarily about negotiating group dynamics and making moral decisions under pressure. In Staaby’s religious studies class, students are exposed to thinkers like Aristotle and Kant to ground them in the basic concepts of moral philosophy. Once they have some theory under their belts, they apply their knowledge of utilitarianism and the categorical imperative to the ethical dilemmas confronting a group of strangers working together to survive in a zombie apocalypse.
“The game is interactive and responds to player input,” explains Staaby. “The choices that you make affect the outcome of the story, and since the game presents the students with ethical dilemmas they have never encountered before, it makes for much more meaningful and engaging discussions. They have to come up with their own solutions, rather than parrot what they’ve read in the media or on the internet.”
The Walking Dead furnishes students with a simulated social environment where they can exercise theory in practice, enjoying the agency to make decisions and reflect on the consequences of their actions.
At one point in the game, an infected woman’s imminent transformation into a zombie conflicts with her religious beliefs. Players have to make the difficult decision as to whether to let her live and “turn” or to assist with her suicide. “I felt really uncomfortable even thinking about discussing this with the class, since euthanasia and suicide are often considered taboo,” says Staaby. “However, I am really glad I went through with it, as this was the most engaging and intense debate we had during the whole project. My students were actively and seemingly automatically applying the ethical theories to their arguments, and it was at this point that I realized how well this method worked.”
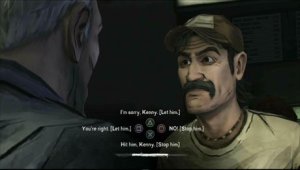
Reflecting on Violent Content
But what about the ethical dilemma of exposing adolescents to violent games in an educational setting? In an atmosphere of conflicting and inconclusive studies, schools tend to steer clear of graphic violence, operating under the implicit presumption that consuming violent media will translate into violent behavior. This abandons children and adolescents to negotiate the almost inescapable world of media violence without the benefit of constructive guidance.
Perhaps a teachable moment—the opportunity to contextualize violence in a frame of empathy and media literacy—is being lost. Staaby concurs: “Instead of shying away from violent content in games and other media, I think it’s important that we discuss why this is so common in the stuff we entertain ourselves with in the first place.” Staaby abides by age-rating guidelines, warns his students about the violence in advance, and has them reflect, discuss, and write about the violent content.
So far, not a single parent has voiced a concern, and Staaby reports that students have been deeply engaged by his use of popular video games. “Never have I experienced my class like when we played The Last of Us or discussed the immensely difficult dilemmas of The Walking Dead. That, at least, has got to count for something.” In an age when engagement in traditional classrooms is losing ground to high-caliber interactive media, this counts for a lot.

Much like a character in The Walking Dead, schools today are confronted with a difficult moral decision: disregard graphic violence in video games and media at the risk of casting our youth adrift, or make allowances for graphic content as a means to productively reflect on and contextualize violence. Ideally, examples like Staaby’s will encourage a greater dialogue about an issue that is becoming too pressing and complex to simply ignore.
Lesson Roundup
Here’s a brief overview of how Staaby uses video games in his practice.
Skyrim: Students explore the vast, rugged medieval fantasy world of this popular RPG, undertaking in-game hunting and gathering for instances of national romanticism. Their findings dovetail into general discussions and reflections on romanticism.
The Last of Us: In this critically acclaimed zombie survival game, the rich narrative and complex characters work with traditional literature lessons. Staaby uses the game to study narrative structure and character arcs, and suggests that it would work well in companionship with a dystopian novel like Cormac McCarthy’s The Road.
The Walking Dead: Ethics theories are introduced piecemeal, just before a relevant dilemma takes place. The game is paused during each dilemma, and students break into groups to discuss the ethical theories and come up with a solution. This allows for the immediate practical application of the theory. Staaby has groups use the polling software Kahoot! to facilitate collective decision-making.
